What are you afraid of? Me, I’m fairly OK with bugs and creepy crawlies but I can’t last five minutes into most horror films. We all have our own personal fears Read more

Science, Curiosity and Life

What are you afraid of? Me, I’m fairly OK with bugs and creepy crawlies but I can’t last five minutes into most horror films. We all have our own personal fears Read more

I must admit, I am fascinated with the effect of music on our bodies, our minds and our emotions. I have always enjoyed music in my own simple way, but I really started to take notice when I had children. Read more

How is your singing voice? I’d love to tell you how good mine is but my kids would be on that like a shot; they are only too happy to tell anyone willing to listen how bad their mum is at singing. So I reserve it for the shower, solo trips in the car… or for tormenting my children. Read more

Well done to six-year-old Daniel who correctly identified the Mystery Creature (again). Daniel really knows his animals! The Mystery Creature was a sea squirt… a very interesting animal, here are just a few reasons why.
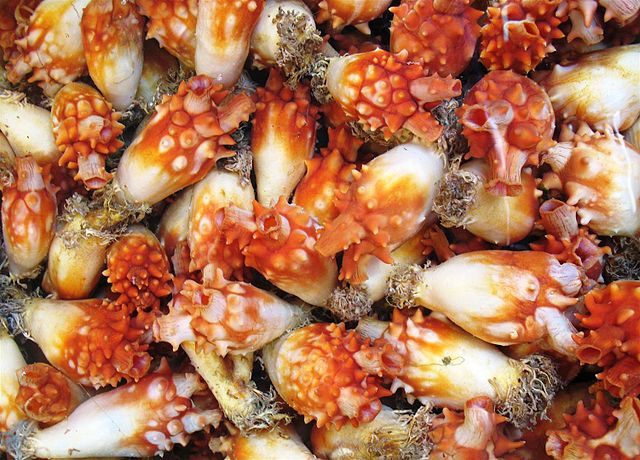

Sea Pineapple: Image credit: Project Manhattan; Image source: wiki commons
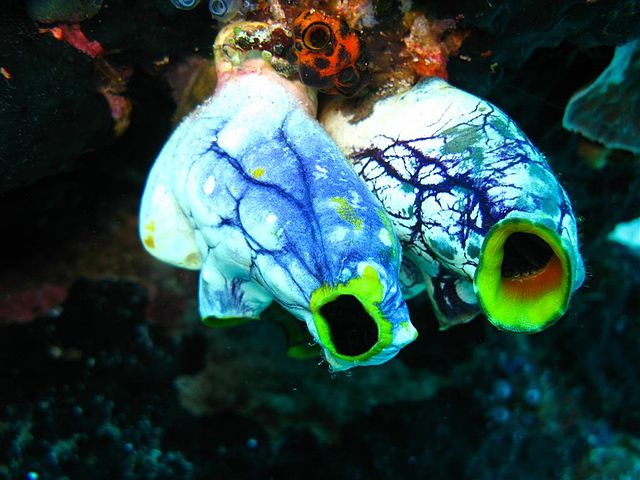
Image credit: Silke Baron; Image source: Wiki commons
Thanks again to Daniel for correctly identifying this Mystery Creature, it really is quite an amazing animal. Check back next week for another new Mystery Creature!

The flying ant invasion of 2015 is upon us, at least in Dublin anyway. It seems they are everywhere and people are naturally a bit put out; but is there an advantage to all of this, and what exactly is the reason for this infestation?
Ants with wings… is this something new?
Not really. There is no one species of winged ants but many species will produce wings during a certain stage of the life cycle of the colony. As we all know, ants like to be busy so if all the chores are done, the larder is full, the young are being tended to and the queen is happy, well there is really only one job left to do…. procreate!
And it is a lot easier to get out there and find the right ant for you if you can grow a pair of wings for a while!
To put it a little more scientifically… in mature, thriving colonies, some eggs, treated under the right conditions, will produce winged ants, both male and female. The females are virgin queens with the potential to start a new colony of their own. The males, well, they have only one thing on their mind!

Why so many?
The newly produced winged ants will remain in the colony until conditions are right for what is referred to as the Nuptial flight. These flights are very weather dependant, requiring warm temperatures with little chance of strong wind or rain. The ants will all leave the colony together in one coordinated flight. This is also synchronised with the flight of ants for neighbouring colonies.
The large numbers serve two purposes….
What happens to the winged ants after the “deed is done”?
After mating both the male and female ants lose their wings.
The female will often mate with several males during the mating process but this will be the only time in her life that she will mate. She stores the male sperm in a pouch in her body called the spermatheca. After mating she will dig a nest to start her own colony… the sex on her offspring is decided by her. All fertilised eggs are female, all non fertilised eggs are male.
When she starts a colony she will produce only female ants, each of which will be infertile and wingless. The queen tends to the first set of eggs on her own but once the worker ants are reared they will tend to her every need and the needs of the colony.
The males? Well they actually die soon after mating… it is their sole purpose.. tough job but what a noble one!
And why is this of any interest to us?
I agree that it is not so pleasant having a face full of crawling ants every time you step out the door but if we look closely at these tiny creatures we have a lot to learn from them; from their engineering mastery to their incredible social networking, ants definitely deserve a second look.
From engineering to traffic control
Firstly, ants are known for their impressive architectural skills. In a very short space of time they can build incredible structures from just a pile of dirt. What is even more impressive is how they seem to work as a unified “machine”, without an apparent hierarchy of “foreman” and “worker”. We have much to learn by cracking to simple “rules” that they follow and we could apply this knowledge to such diverse areas as engineering, traffic control, cell biology and robotics.
Strengthening our social standing
Ants are incredibly social creatures. Without their social interaction, they face a much shorter life span and even seem to lose the ability to digest food. Working together they can achieve the unthinkable.
They are eusocial creatures, along with termites and some bees, wasps and aphids. A eusocial society usually expressed division of labour, an overlap of generations to help with care of the young and adults sharing living space. The advantages of such living arrangements include better protection (safety in numbers) and a more likely chance for a regular food supply. It can be argued that we humans are also eusocial creatures in a somewhat fragile existence and can better address any precarious imbalances with a greater understanding of how eusocial insects, such as the ant, sustain and strengthen their social system.
Learning how our brain works
Science shines a spotlight on the similarities between the communication within an ant colony and the workings of the human brain. It seems both operate very efficiently without any one direct control centre and, just like no two brains are exactly alike this is also true for each ant colony.
Maybe all this will show these tiny creatures in a new light and make their hair tangling flightless frustrating at this time of year.
Have you spotted them en mass in your area? Don’t despair, it doesn’t last long and, for the ant it is a life or death event, for us humans, it is a small inconvenience.
***
And a little something else … I am delighted to see my blog listed among some favourite bloggers in the Boots Maternity and Infant Parenting Blog Awards 2015. If you like what I do here and have a minute to spare I’d really appreciate your vote; You just need to click the image below and scroll down to the “Best Parenting Blog” section under “For the Family”; Many thanks!

From the moment I get up in the morning the questions start rolling…. the three year old is going through a “what happens if” phase with an alarmingly gruesome theme these days; “Mammy, what will happen if your eye ball falls out and you stand on it and squash it?” is just one of his recent gems! Before I have even had my morning cuppa I have attempted to answer a fair whack of questions. The process continues throughout the day… from the back of the car, while we do the shopping, during meals and all the way through to bedtime… he can literally fall asleep mid question!
But why the incessant bombardment of questions?…
There are over 100 billion cells in the brain of a newborn child. These cells need to start forming networks and connections with each other or else they will be “deleted” by the body in favour of more active cells . It is the child’s interaction with its surroundings and its social contact that greatly influence the amount of connections made within its brain.
The brain of a three year old is two times more active than that of an adult!

…. just a thought!